|
The Newfoundland and Labrador Hydro Group of Companies will help sustain a diverse and healthy
environment for present and future Newfoundlanders and Labradorians by maintaining a high standard
of environmental responsibility and performance through the implementation of a comprehensive
environmental management system. The following guiding principles set out the Hydro Group's
environmental responsibility:
-
implement reasonable actions for prevention of pollution of air, water, and soil and minimize the
impact of any pollution which is accidental or unavoidable;
-
use energy as efficiently as possible during the generation, transmission, and distribution of
electricity, and the operation of its facilities, and promote efficient use of electricity by customers;
-
maintain a state of preparedness in order to respond quickly and effectively to environmental
emergencies;
-
recover, reduce, reuse and recycle waste materials whenever feasible;
-
use the Province's natural resources in a wise and efficient manner;
-
audit facilities to assess potential environmental risks and continually improve environmental performance;
-
integrate environmental considerations into decision-making processes at all levels;
-
empower employees to be responsible for the environmental aspects of their jobs and ensure that they have
the skills and knowledge necessary to conduct their work in an environmentally
responsible manner;
-
periodically report to the Board of Directors, Executive Management, employees, government agencies, and the
general public which we serve on environmental performance, commitments and activities;
-
comply with all applicable environmental laws and regulations, and participate in the Canadian Electricity
Association's Environmental Commitment and Responsibility Program;
-
monitor compliance with environmental laws and regulations, and quantify predicted environmental impacts of
selected activities on the environment;
-
respect the cultural heritage of the people of the Province and strive to minimize the potential impact of
Corporate activities on heritage resources.
|
|
Newfoundland and Labrador Hydro (Hydro) is a Crown Corporation, owned by the Province of
Newfoundland and Labrador. With a dedicated workforce of 1190 full-time equivalents, including
Churchill Falls (Labrador) Corporation (CF(L)Co.), Hydro generates, transmits and distributes
electrical power and energy to utility, industrial and residential customers
throughout the Province.
Founded in 1954 as the Newfoundland Power Commission, with a mandate to promote rural
electrification, Hydro was established as a Crown Corporation in 1975 and is currently governed by
the Hydro Corporation Act and the Electrical Power Control Act. Hydro has a mandate to deliver
reliable, least cost energy to the residents and industry in Newfoundland and Labrador.
Hydro is the parent company of the Hydro Group of Companies (Hydro Group) comprised of Newfoundland
and Labrador Hydro, Churchill Falls (Labrador) Corporation Limited, Lower Churchill Development
Corporation Limited (LCDC), Gull Island Power Company Limited (GIPCo.), and Twin Falls Power
Corporation Limited (Twin Falls).
The Hydro Group's installed generating capacity is the fourth largest of all utility companies in
Canada. Our power generating assets include 10 operating hydroelectric plants, one oil-fired plant,
four gas turbines, 28 diesel plants and the Churchill Falls Hydroelectric Generating Station, the
largest underground powerhouse in the world with a rated capacity of 5,428 megawatts (MW) of power.
Hydro also maintains over 4,700 km of transmission lines and over 3,600 km of lower voltage
distribution lines.
Every year, Hydro generates over 80 per cent of the electrical energy consumed by Newfoundlanders
and Labradorians. We are an integral part of the Province's electrical system. Hydro also distributes
power directly to 35,000 customers in rural Newfoundland and Labrador, which represents about 15 per
cent of the Province's electrical consumers. The challenge of providing power to rural, and often
remote, communities that experience challenging weather conditions cannot be overstated. It is a
balancing act of cost and reliability to meet the expectations of our customers. We continue to strive
for operating efficiencies while providing quality service to our customers and making the right
strategic investments to maximize performance.
Hydro engaged in a number of important initiatives and achieved significant milestones in 2003. From
a year of record sales, another multi-faceted rate hearing, to the commissioning of the Granite Canal
Hydroelectric Generating Station, the past year has certainly reflected the complexity of our operating
environment. Despite the challenges, we are proud of our record of service and we will strive for
continual improvement in all areas of our operation as we meet the energy needs of Newfoundland
and Labrador.
|
|
 The Newfoundland and Labrador Hydro Group of Companies (Hydro Group) maintains a strong
commitment to environmental responsibility. That commitment is evident in a number of projects
that were completed this past year. The new Fish Habitat Compensation Facility, constructed in
conjunction with the development at Granite Canal, has set the benchmark for such projects across
the country. A Continuous Emissions Monitoring System has been installed at the Holyrood Thermal
Plant to assist in environmental monitoring and unit efficiency. The plant also hosted over
200 members of the public to its fifth annual Open House during Environment Week in 2003. We are
committed to ongoing communication with local residents. The Holyrood Community Liaison Committee
has been in place now for over five years and enables plant staff to meet with local representatives,
discuss concerns and share operational and environmental data.
The Newfoundland and Labrador Hydro Group of Companies (Hydro Group) maintains a strong
commitment to environmental responsibility. That commitment is evident in a number of projects
that were completed this past year. The new Fish Habitat Compensation Facility, constructed in
conjunction with the development at Granite Canal, has set the benchmark for such projects across
the country. A Continuous Emissions Monitoring System has been installed at the Holyrood Thermal
Plant to assist in environmental monitoring and unit efficiency. The plant also hosted over
200 members of the public to its fifth annual Open House during Environment Week in 2003. We are
committed to ongoing communication with local residents. The Holyrood Community Liaison Committee
has been in place now for over five years and enables plant staff to meet with local representatives,
discuss concerns and share operational and environmental data.
There have been many successes this year and none that makes us more proud than having all our
divisions receive ISO 14001 certification. This is a major accomplishment and certification provides
us with a solid framework for environmental management and continual improvement.
Our commitment to the environment can also be seen throughout all Hydro Group departments and
divisions, and all our employees are aware of our Environmental Policy and Guiding Principles. Leading
our environmental programs is our Environmental Services and Properties Department; that is comprised
of an exceptionally talented team of ecologists and technicians who ensure that Hydro is meeting its
environmental objectives. I would like to commend them for their ongoing commitment to their work, the
environment and our organization.
The nature of our business - power generation and transmission - often raises environmental concern.
We are committed to managing our operations to reduce our environmental impact while balancing our
mandate to provide our customers with cost-effective and reliable power. I encourage you to read our
Environmental Performance Report and as always, I welcome your feedback.
|
|
-
Hydro's Transmission and Rural Operations Division met all the requirements for ISO 14001
certification in 2003. All Hydro's Environmental Management Systems (EMS) are now registered. This is
a significant accomplishment for all employees and reflects our commitment to responsible
environmental management.
-
As part of its continuing commitment to the environment, and in support of our EMS, the development at
Granite Canal included the construction of a
45,000 m2 - Fish Habitat Compensation Facility. This
facility provides spawning and rearing habitat for landlocked salmon and brook trout, and includes a
number of innovative features in its construction and design.
-
Hydro invested over $1.5 million at its Holyrood Thermal Generating Station in Continuous Emissions
Monitoring equipment and upgraded Ambient Air Monitoring Systems. These investments will allow the
plant to address environmental and efficiency concerns in a more effective and timely manner.
-
Hydro completed 13 Phase I Environmental Site Assessments (ESA) on properties we own and operate as part
of a long term plan ESA Program.
-
Combined increases in hydraulic generation and energy purchases, offset by some modest increase in
Island system sales, resulted in an 18 per cent reduction in production from Holyrood to 2,061 GWh. This
resulted in a reduction of No. 6 fuel oil consumption to 3,074,000 barrels. The total emission of carbon
dioxide (CO2), sulphur dioxide
(SO2), and nitrogen oxide (NOX) therefore
decreased in 2003.
-
The rate of particulate emissions at high load has improved dramatically over the past 10 years from 62.5
to 14.6 grams per second. A decrease was also evident in 2003. Hydro has achieved these improvements as a
result of technological improvements in fuel burners, increasing operating efficiencies, and optimizing the
use of the plant for the electrical needs on the Island Interconnected System.
-
Hydro partnered with several organizations last year including Conservation Corp of Newfoundland and
Labrador, Newfoundland and Labrador Construction Safety Association (NLCSA), Climate Change Education
Centre (CCEC), Hydro-Quebec, and the Department of Fisheries and Oceans to pursue
environmental programs.
|
|
 Many employees within the Hydro Group play a significant role in environmental protection by virtue
of the tasks they perform on a daily basis. We are proud of their competence and commitment.
Many employees within the Hydro Group play a significant role in environmental protection by virtue
of the tasks they perform on a daily basis. We are proud of their competence and commitment.
We also have a group of environmental specialists whose role is to provide leadership, advice, and technical
services to the operating and service parts of the business, and Executive Management. The Environmental
Services and Properties Department in St. John's is comprised of people with diverse backgrounds in
environmental technology and management and are responsible for:
-
Reporting - prepare a wide-range of reports to communicate the Hydro Group's environmental performance
to internal and external stakeholders;
-
Environmental Assessment - assess actual or predicted environmental impacts of the Hydro Group's
activities, operations, and past practices on the natural environment, and recommend ways to mitigate
these impacts;
-
Auditing - determine the extent of the Hydro Group's compliance with obligations and commitments, and
conformance of EMSs to the ISO 14001 standard;
-
Standard Setting - define environmental performance standards for the Hydro Group, which clarify its
Environmental Policy and Guiding Principles;
-
Tracking Legislation and Issue Development - monitor the development of new legislation, emerging
environmental issues, management techniques and technologies;
-
Environmental Services - provide technical expertise to undertake or manage specialized environmental
tasks that are required by operational and service departments.
This core group of environmental specialists reflects the commitment of the Hydro Group to its
responsibility to excellence in environment management.
|
|
The number and diversity of environmental challenges facing large companies require a structured
and consistent management approach. The Hydro Group has chosen the ISO 14001 Environmental Management
System (EMS) standard developed by the
International Organization for
Standardization to manage its environmental aspects. This decision has resulted in continual
improvement of environmental performance, while fulfilling our mandate to provide our customers with
cost-effective and reliable power.
The six designated management areas (Figure 1) within the Hydro Group are now managing their
environmental aspects through EMSs consistent with ISO 14001. Each EMS is certified and registered by
a third party, Quality Management
Institute (QMI). We are very proud of this accomplishment.
General accomplishments resulting from the Environmental Management Programs (EMP) in the Management
Areas in 2003 are noted below, however, details will be highlighted in the appropriate sections of
this report.
The Corporate Management Area consists of Executive Management and a Committee of Senior Managers. The
goal of this Management Area is to co-ordinate the development and maintenance of the overall EMS for
the Hydro Group. Although each EMS is managed independently, a common and consistent environmental policy
and principles sets the standard, and periodic reviews of activities and issues are conducted.
One of the most significant decisions related to the overall program was to amalgamate the individual
EMSs for the three regions of the Transmission and Rural Operations (TRO) Division into one. This is
expected to improve the efficiency of managing the EMS and allocation of resources to the appropriate
issues.
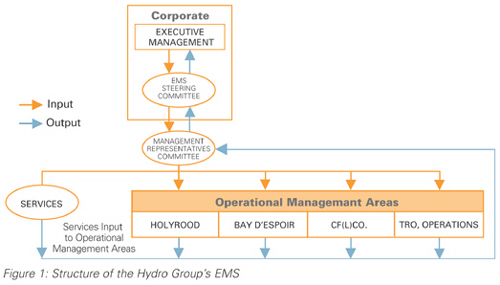
HOLYROOD
The Holyrood Thermal Generating Station is a 490 Megawatt (MW) thermal generating station located near
Holyrood, Conception Bay. Holyrood's EMS was initially registered in January 1999 and obtained
re-registration in 2002.
In 2003, Holyrood made progress on 11 Environmental Management Programs (EMP). These EMPs resulted in:
- a reduction in auxiliary power used at the plant;
- optimum unit efficiency;
- no reportable spills of controlled substance;
- removal of PCB waste and asbestos from the plant; and
- recycling of scrap metal.
BAY D'ESPOIR
The Bay d'Espoir Management Area consists of seven existing generating stations on the Island with an
installed capacity of 899 MW. In 2003, an eighth station constructed at Granite Canal (40 MW) was
commissioned and its environmental aspects incorporated into the EMS. The EMS was registered in 1999
and re-registered in 2002.
There were six EMPs worked on in 2003, which resulted in the following successes:
- improvement of generating equipment to reduce oil loss into the environment;
- no reportable spills; and
- enhancement of fuel storage facilities at remote locations throughout the system.
CHURCHILL FALLS (CF(L)CO.)
The Churchill Falls Hydroelectric Generating Station in Labrador has an installed capacity of 5,428 MW.
Associated with this development is approximately 1,200 km of high voltage transmission line, an airport,
and the Town of Churchill Falls. Environmental aspects of all these facilities are included in the EMS.
The environmental aspects of the moth-balled Twin Falls hydroelectric station are also managed
through CF(L)Co.'s EMS. The EMS was registered in 1999 and was re-registered in 2002.
The EMPs resulted in the following accomplishments:
- remediation of six stream crossing sites, and fabrication of three bridges to reduce the potential
impact on fish populations;
- reduction of oil loss through improved preventative and corrective maintenance;
- increased recycling of turbine oil;
- reduction of the number of reportable spills to one;
- improvement of environmental management at Twin Falls by installing remote detection equipment and
completing an environmental site assessment;
- expansion of the use of environmentally friendly turbine gate grease; and
- removal and recycling of 90 tonnes of scrap overhead ground wire from the high voltage transmission line.
TRANSMISSION AND RURAL OPERATIONS (TRO)
The TRO Division consists of three regions that manage 23 rural, isolated diesel generating plants
(30.2 MW), three gas turbine plants (125 MW), and approximately 8,300 km of transmission and distribution
lines, and associated switching stations. The three regions share a common EMS, which was registered
in 2003.
In 2003, eight environmental management programs resulted in:
- the study of alternative forms of applicators to reduce the use of herbicides for vegetation control;
- improved documentation of equipment that may contain PCB in order to develop plans for sampling and
replacement;
- improved tracking and management of treated transmission and distribution poles removed from service; and
- assessment of fording sites on access trails associated with transmission lines in Labrador to reduce the
potential impact on fish and fish habitat.
The Services Management Area includes services (eg. engineering design, system planning, environmental
services, procurement) and facilities (eg. Hydro Place, telecommunication sites) that support the
operation of the business. The Services EMS includes nine diverse environmental management programs. The
Services EMS was registered in 2000 and was recommended for re-registration in 2003.
The following accomplishments in 2003 are noteworthy:
- the halon replacement program was completed to the degree possible;
- 13 Phase I Environmental Site Assessments were completed on selected properties owned and operated by
the Hydro Group to identify any potential contamination requiring further investigation;
- energy efficiency from historical levels improving; and
- water management procedures were amended to accommodate the needs of the Granite Canal Fish Habitat
Compensation Facility.
|
|
The Holyrood Thermal Generating Station's wastewater treatment plant treats the wastewater resulting
from the combustion of fuel, and runoff from the solid waste landfill. Constituents of the wastewater
from the plant are measured and compared to regulatory limits. Once all aspects of the wastewater are
compliant, the wastewater is released into the environment. In 2003, a total of 6.22 million litres of
wastewater was treated and discharged, which is a decrease from the 7.26 million litres of wastewater
processed in 2002.
Hydro relies on both hydroelectric and thermal generation to meet customer needs. The operation of
Holyrood is highly dependent on the availability of water in our hydroelectric reservoirs. Water levels
in our reservoirs vary from year to year with the amount of precipitation and runoff. As water levels
increase in the reservoirs, the demand on thermal generation decreases, as well as the associated air
emissions.
Hydraulic production was 4,338 GWh in 2003, up 8.4 per cent from 2002. This was the result of increased
reservoir inflows and the addition of the Granite Canal Hydroelectric Generating Station to the system.
Purchases of energy also increased by 79.5 percent to 295 GWh, primarily a result of new non-utility
generating sources being brought into service by Corner Brook Pulp and Paper and the Exploits River Hydro
Partnership.
The combined increases in hydraulic generation and energy purchases offset by some modest increase in
Island system sales resulted in an 18 per cent reduction in production compared to 2002 from Holyrood to
2,061 GWh. This resulted in a reduction of No. 6 fuel oil consumption to 3,074,000 barrels. The total
emission of carbon dioxide (CO2), sulphur dioxide
(SO2), and nitrogen oxide (NOX) therefore
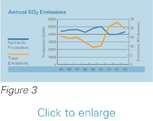
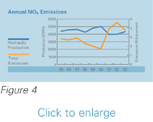
decreased in 2003. Figures 2, 3 and 4 show the relationship between hydraulic production and atmospheric
emissions.
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
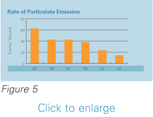
The average rate of particulate emissions at high load at Holyrood was measured in 2003, and comparative
results from previous years are shown in Figure 5. Improvements were achieved in recent years as a result
of technological improvements in our fuel burners, by increasing operating efficiencies, and by optimizing
the use of the plant for the electrical needs on the Island Interconnected System.
|
|
Stack emission testing, conducted every two years, was performed on the three generating units at Holyrood
during 2003. The tests monitor particulate, particulate particle size, metals, sulphates,
SO2, NOX, carbon
monoxide (CO), and CO2 in the exhaust-gas.
Test results are reported to the provincial Department of Environment and Conservation to satisfy an
existing agreement, and are used for on-site evaluation, the annual report on air emissions, and
exhaust-gas modeling. The results also provide data on our initiatives to improve overall unit performance
and efficiency.
In 2003, Continuous Emission Monitors (CEM) were installed on the three units at the Holyrood Thermal
Generating Station. The CEMs are intended to continuously monitor
SO2, NOX, CO,
CO2, and oxygen (O2) in
the exhaust-gas. The data collected will be used to monitor and improve overall unit performance
and efficiency.
|
|
The majority of waste produced at our operating facilities is disposed of through government approved
waste management systems, and do not require special handling and disposal. Below is information on
special waste handling and recycling activities.
The Hydro Group operates two approved PCB waste storage facilities located in Bishop's Falls and
Churchill Falls.
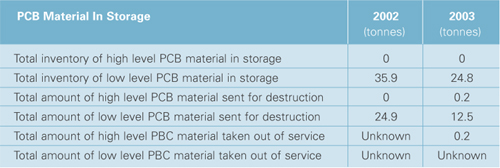
BISHOP'S FALLS
In 2003, 1.4 tonnes of low level PCB material was placed in storage at the Bishop's Falls facility. This
brought the total quantity of low level PCB material at this facility to 37.3 tonnes. Approximately 12.5
tonnes was removed from storage during 2003 and destroyed. Therefore, the total quantity of low level PCB
material in storage as of December 31, 2003 was 24.8 tonnes. As of December 31, 2003, there was no high
level PCB material in storage (Table 1), however, approximately 0.2 tonnes was sent for destruction
in 2003.

It is recognized that some older equipment such as capacitors and fluorescent light ballasts, which may
contain high levels of PCB, remains in service. It is estimated that there is less than one tonne of such
PCB material remaining in service.
It is known that a portion of the older distribution transformers in service throughout the system contain
oil which is contaminated with PCB to a level greater than 50 ppm. Hydro has initiated a multi-year
program to reduce PCB contaminated equipment in service. This program involves the identification, testing,
and removal from service or refurbishment of all electrical equipment with a PCB level greater
than 50 ppm.
CHURCHILL FALLS (CF(L)Co)
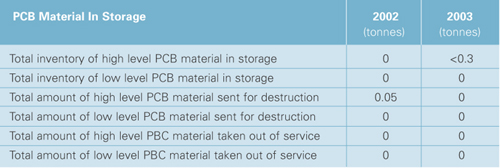
Table 2 provides an inventory of PCB material in storage and in service as of December 31, 2003, in
Churchill Falls. At present, the total amount of low level and high level PCB material in storage is
less than 0.3 tonnes. There was no PCB material sent for destruction in 2003. PCB material known to be in
service are ballasts and capacitors, however, there is no inventory completed of this electrical equipment
to date. Once draft new PCB regulations are finalized, CF(L)Co will compile the inventory of PCB material
equipment as required.

INSULATING OIL
The quantities of electrical insulating oil reused and recycled by Hydro and CF(L)Co. in 2003 was
approximately 282,000 litres.
In 2003, approximately 128,400 litres of insulating oil, which did not meet the specification for reuse,
was supplied to a third party for energy recovery.
LUBRICATING OIL
Waste lubricating oil from throughout Hydro's operating systems is captured and supplied under contracts
to government certified waste oil handlers for recycling or energy recovery. The volumes of lubricating
oil provided to these parties in 2003 totaled approximately 107,600 litres.
SCRAP METAL
CF(L)Co., again in 2003, completed a successful year in its scrap metal recycling program. Approximately
81 tonnes of overhead ground wire from the 735 KV line and 91 tonnes of miscellaneous scrap metal from
outlying properties was recycled.
Hydro's Generation Division put a large focus on scrap metal recovery in 2003. Approximately eight tonnes
of condemned road culverts, structural steel, components of generating units and electrical panels that
had been accumulating for years was collected and sent for recycling. This compares to approximately 0.7
tonne recycled in 2002.
Our Transmission and Rural Operations Division, through auctions, sent approximately 54 tonnes of scrap
transformers and conductor to metal recyclers in 2003.
TREATED WOOD
Treated wood is essential for the reliability of wood pole transmission and distribution line systems
since treated wood has a longer service life than untreated wood. We recognize that treated wood must be
used and managed in a responsible manner. Whenever Hydro uses treated wood, specific guidelines are
followed to minimize the potential impact of preservatives on the surrounding environment. The potential
for wood preservative contamination during installation, maintenance and disposal are always
considered.
In 2003, Hydro implemented a new record keeping system in the Central Region to accurately track wood
poles. The system will be implemented in the other two regions in 2004. Approximately 80 percent of all
material removed from service is given to individuals or groups outside of Hydro for reuse, 15 percent
was taken from work sites before it could be transported to a storage area, and the remaining five percent
was held in storage for testing and recycling. Approximately 90 percent of this material was treated with
pentachlorophenol (Penta), eight percent was treated with copper chromated arsenate (CCA) and the remaining
two percent was treated with creosote. Disposal of treated wood at landfill sites is only considered if the
material is deemed unsalvageable. In 2003, approximately two tonnes of Penta treated wood was taken to
landfills for disposal.
Despite all reasonable efforts, Hydro continues to experience problems with the loss of salvageable
treated wood from work sites before it is moved to secured marshalling yards and/or depots. It is
speculated that this material is being taken by individuals who are taking advantage of the opportunity
to obtain building material that they believe is destined to be discarded as waste. Hydro will be
implementing measures to make the public aware that the use of this material for unauthorized purposes
can be hazardous.
In 2003, Hydro purchased 30 CCA, 15 Penta, and two untreated transmission poles, and 938 CCA, 64 Penta,
and 32 untreated distribution poles.
BOILER ASH
Boiler ash is produced at the Holyrood Thermal Generating Station as a result of the combustion
process. During 2003, approximately 600 tonnes of fuel ash was produced and disposed of at an on-site,
controlled solid waste landfill.
|
|
The generation and delivery of electricity requires the handling and use of a variety of potential
environmental contaminants such as fuel oils, lubricating oils, and chemicals. In 2003, the Hydro Group
used approximately 15 million litres of diesel fuel and 488 million litres of No.6 fuel oil to generate
electricity. While we strive to reduce the potential for leaks and spills, incidents can and do occur,
most often the result of equipment failure, unanticipated hazards, and occasionally, human error. Being
prepared for such an incident is critical to mounting a quick and effective response to minimize impacts
on people and the environment. We have developed Environmental Emergency Response Plans (EERP) to quickly,
effectively and safely deal with such incidents. Within the Hydro Group, all personnel who handle or work
around petroleum products receive training related to the EERP and, when applicable, specific operating
procedures have been developed to facilitate the safe handling of the products used.
In 2003, our personnel responded to 11 reportable spills or leaks involving petroleum products. Reportable
spills or leaks are defined as those that exceed 70 litres; or a spill or leak, regardless of quantity,
that has the potential to contaminate nearby property or enter a waterbody or sewer; or a release, or
potential release, of a PCB contaminated material. The volume of petroleum product involved ranged from
less than one litre to 1,300 litres. In each case, the incident was reported, and appropriate containment
and clean-up procedures were undertaken to remediate the affected area.
Six spill incidents occurred as a result of the failure of electrical equipment, with one incident
involving low-level PCB contaminated transformer oil. Piping leaks accounted for three spill incidents,
while human error and equipment failure accounted for the remaining two. Personnel addressed all the
incidents by containing the incident and initiating appropriate recovery and cleanup procedures. All waste
material was contained and appropriately disposed.
We also attempted to document, investigate and respond to all complaints, or expressions of concern,
on environmental matters from the public and government agencies.
In 2003, we responded to several public complaints related to environmental aspects of our operations.
The majority came from people residing close to the Holyrood Thermal Generating Station, and were
related to atmospheric emissions, excessive noise, and odour. All complaints were investigated and
results were provided to the people involved.
|
|
In 2000, the Hydro Group implemented an Environmental Site Assessment (ESA) Program to assess all
properties we own or operate. The process that was adopted for the program is depicted in Figure 6.
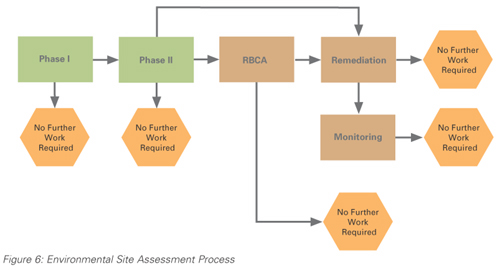

The objectives of the ESA program are to:
- evaluate the potential for environmental contamination;
- undertake sampling to characterize and delineate any contamination;
- assess the potential risks and liabilities associated with any contamination identified;
- identify sites requiring monitoring or remediation; and
- develop and implement remediation programs when necessary.
Since the inception of the ESA program in 2000, the sites of all rural isolated generating sites have
been assessed. These are the sites of the highest environmental risk based on the throughput of potential
contaminants. The program will now focus on facilities with less hydrocarbon storage capacity and,
therefore, potential risk such as terminal stations, material storage yards, and line depots.
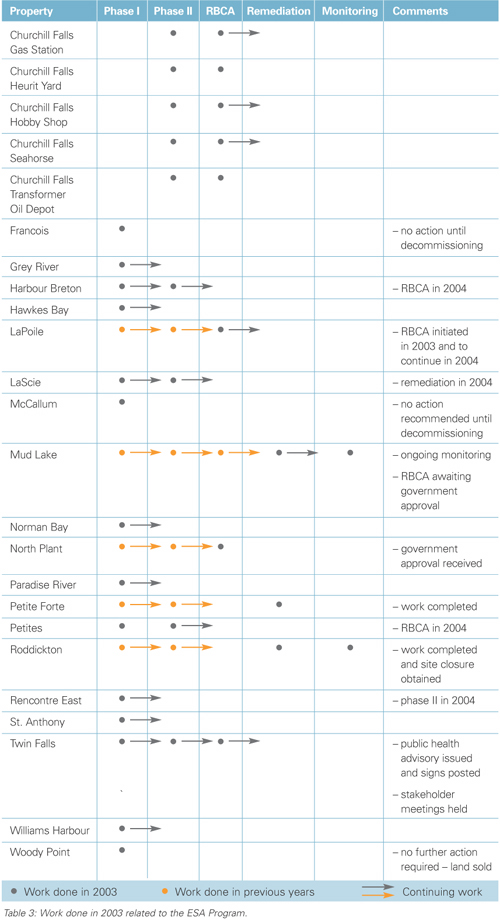
Table 3 shows the ESA work that was accomplished in 2003 and future plans, if any, for the site.
|
|
Hydro completed construction of the Granite Canal Hydroelectric Development during the summer of
2003 and commenced formal operation of the facility in August. As part of the environmental assessment
for the project, fish and caribou were identified as the two significant environmental aspects. To
address concerns associated with these, Hydro committed to compensating for 444 units
(100 m2 = 1 unit)
of salmonid spawning and rearing habitat that would be altered, disrupted or destroyed as part of
the project and to monitor migration of the Buchan's Plateau Caribou Herd in the vicinity of the
Project site.
GRANITE CANAL FISH HABITAT COMPENSATION FACILITY
 Environmental assessment of the Project identified that a principle spawning area for fish inhabiting
Meelpaeg Lake would be de-watered. To compensate for the habitat to be altered, disrupted or destroyed,
Hydro incorporated construction of 444 units of salmonid spawning and rearing habitat into the project
design.
Environmental assessment of the Project identified that a principle spawning area for fish inhabiting
Meelpaeg Lake would be de-watered. To compensate for the habitat to be altered, disrupted or destroyed,
Hydro incorporated construction of 444 units of salmonid spawning and rearing habitat into the project
design.
The Fish Habitat Compensation Facility (FHCF) that was constructed included a main channel and two side
channels, called Compensation Creek, totaling 297 units of habitat designed for utilization by ouananiche
and brook trout. Habitat constructed in the tailrace delta consisted of 139 units. A small diversion
channel contained eight units of habitat designed for brook trout utilization, and fish passage to a
residual watershed containing 23 units of salmonid spawning and rearing habitat.
Immediately upon completion of construction of the FHCF, Hydro implemented a monitoring program
designed to confirm the structural stability of the facilities and their utilization by landlocked salmon
and brook trout. Initial, non-intrusive, biological and physical monitoring commenced during the fall of
2003. Initial monitoring confirmed utilization of Compensation Creek and the tailrace delta habitat by
salmonids for spawning. The comprehensive biological and physical monitoring program will commence
during 2004. Monitoring will continue for at least six years.
Recent correspondence from the Regional Director General for DFO, Newfoundland Region to Hydro stated
development and implementation of the Granite Canal Fish Habitat Compensation Facility has been
depicted as an exceptional example of Hydro's commitment towards ensuring the conservation and
protection of fish and fish habitat in the Province and throughout the country.
BUCHAN'S PLATEAU CARIBOU HERD MONITORING
As part of the Environmental Assessment for the project, Hydro monitored migration of the Buchan's
Plateau Caribou Herd in the vicinity of the project site for two years prior to construction, and
monitoring continued during the three years of construction. Hydro is also committed to monitoring two
years post-construction. The herd's annual migration is from the south coast of Newfoundland between
Bay d'Espoir and LaPoile to the Buchan's Plateau, which is known to be their principle calving grounds.
This annual migration to and from these areas is approximately seven to nine kilometers west of the
project site. Straggler caribou are present in the project area for much of the year.
Results from the construction phase monitoring of the herd have been compared to the pre-construction
data. This comparison indicated that the migration patterns during the pre-construction and construction
periods remained similar, and that construction activity had little or no effect on migration through the
project area. Monitoring data collected to date confirm the prediction during the environmental assessment
that impacts on caribou would be minor, insignificant, direct, negative and short term. Post-construction
monitoring data collected will continue to be compared with earlier findings.
|
|
A priority for the Hydro Group is to build and cultivate partnerships with other agencies and
organizations to achieve common environmental objectives. These partnerships maximize human and
financial resources to generate a body of knowledge and experience that can be used for environmental
decision-making in a variety of applications.
The Hydro Group has a long-standing relationship with the
Conservation
Corps of Newfoundland and Labrador. In 2003, Hydro sponsored a Green Team of four local youth who
worked with researchers from Parks Canada and Memorial University to help identify the location of
rare plant species located on the Limestone Barrens of the Great Northern Peninsula. The team also
conducted community and land use surveys, as well as information sessions to develop and provide an
interpretive tour of the Barrens.
In conjunction with the
NLCSA, Hydro developed a training course for
contractors on environmental protection within construction sites. We advised potential contractors that
having the course would be a condition of doing work for Hydro after January 1, 2004. By the end of 2003,
approximately 104 people representing 55 companies had completed the course. This partnership is
expected to improve environmental performance at all construction sites in the province, not only those
initiated by the Hydro Group.
Hydro and DFO conducted a joint study to track the migration of fish in the area of the Granite Canal
hydroelectric project. Scientists are using radio telemetry to follow the movements of approximately 90
fish throughout the year. Hydro's main objective is to document the use of the Fish Habitat Compensation
Facility constructed as part of the project. Invaluable information on habitat requirements by ouananiche
and brook trout is also being obtained that can be used for the management of inland fish in situations
throughout the Province.
Hydro Québec has been undertaking extensive studies on the production of greenhouse gas emission from
their reservoirs. In the summer of 2003, Hydro collaborated with the scientists at Hydro Québec to take
similar measurements at reservoirs in the Bay d'Espoir system. Preliminary analysis is complete and a final
report will be available in 2004.
Hydro continued its partnership with the Conservation Corps to support the
CCEC.
The CCEC develops and delivers innovative education and outreach programs to educate the public on climate
change and influence how they respond to this environmental concern.
|
|
